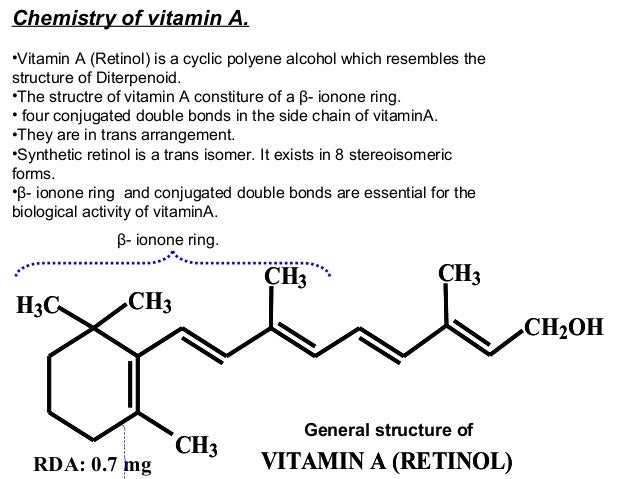
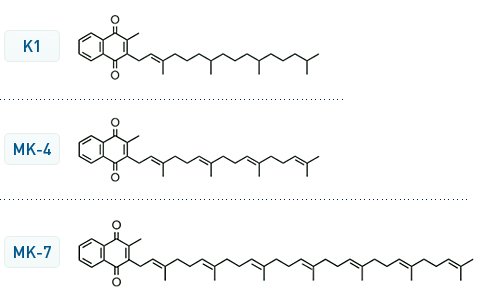
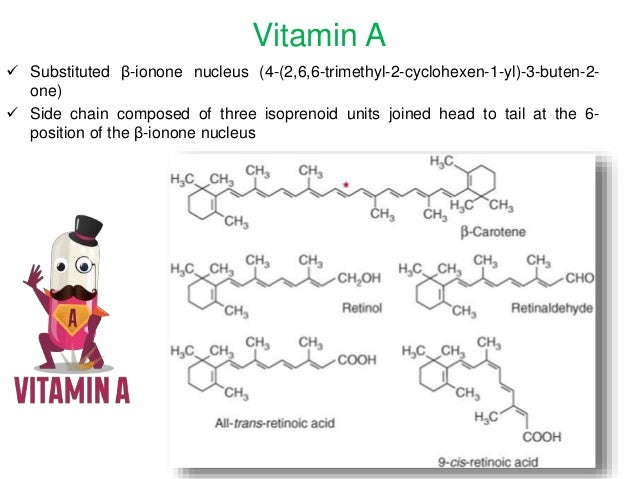
Vitamin A D E K Structure

Vitamins a to e including a range of b vitamins and vitamin k.
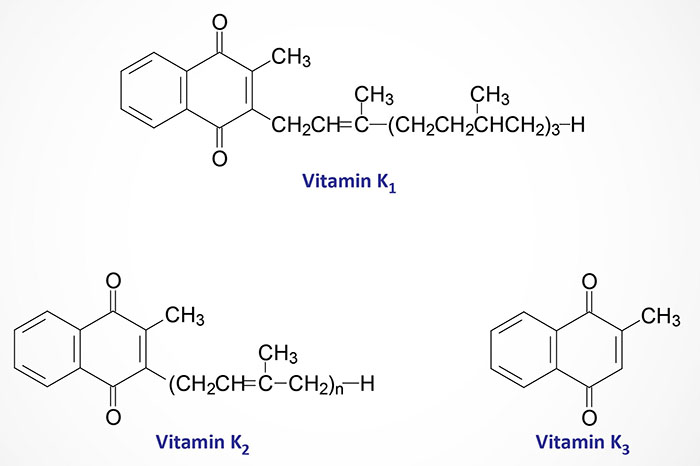
Vitamin a d e k structure. Foods that contain these vitamins will not lose them when cooked. A these vitamins are normally highly unstable molecules and are stabilized by fatty acids b these vitamins require fats for their absorption and transport c fats provide the energy required to move these large molecules across the intestinal wall d these vitamins are found. From this figure how is vitamin k involved in blood clotting. There are four fat soluble vitamins in the human diet.
Promotes proper immune function and assists in calcium absorption and bone growth. Although a micronutrient it enhances the metabolism of macronutrients like proteins carbohydrates and fats. Vitamins are biologically important. For example vitamin b7 biotin was previously referred to as vitamin h.
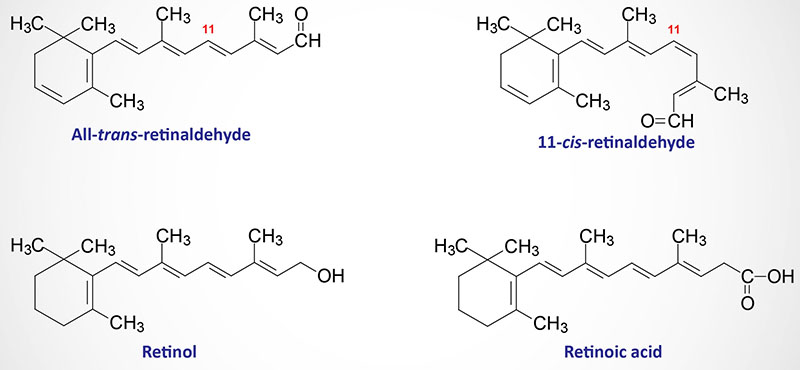
The body does not need these every day and stores them in the liver when not used. Vitamin a is needed by the retina of the eye in the form of retinal which combines with. Fat soluble vitamins vitamin a d e and k. Vitamins refer to any of a group of organic compounds which are essential for normal growth and nutrition and are required in small quantities in the diet.
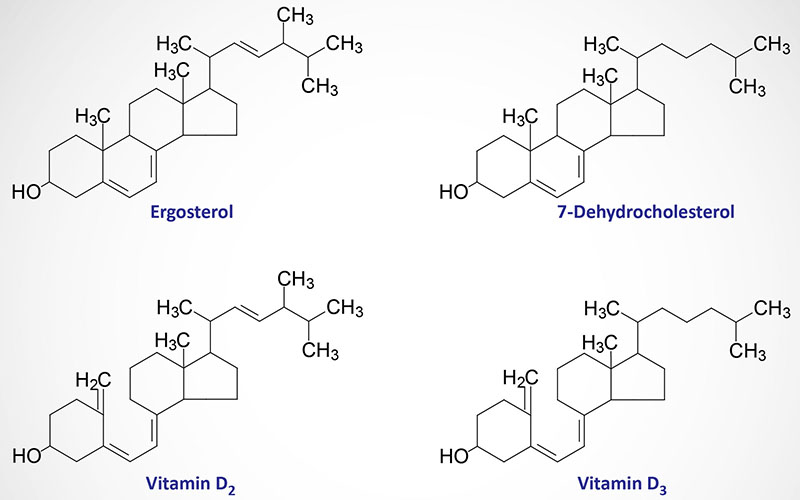
Fat soluble vitamins are vitamins a d e and k. Small amounts of vitamins a d e and k are needed to maintain good health. The slightly odd gap in lettering between e and k is a consequence of changes in designations of vitamins. The process whereby cell changes occur in structure and function leading to specialization is known as cell.
It is important for growth and development for the maintenance of the immune system and for good vision. Currently there are 13 recognised vitamins. Vitamin e deficiency which is rare and usually due to an underlying problem with digesting dietary fat rather than from a diet low in vitamin e can cause nerve problems. Megadoses of vitamins a d e or k can be toxic and lead to health problems.
Vitamin e is a group of eight fat soluble compounds that include four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. Which of the following is a good source of vitamin e. A d e and k. This guide examines their health benefits functions and main dietary sources.
Vitamin a is a group of unsaturated nutritional organic compounds that includes retinol retinal and several provitamin a carotenoids most notably beta carotene. Vitamin a has multiple functions. The body absorbs these vitamins as it does dietary fats. Vitamin k helps to produce the blood clotting protein prothrombin.
Assists immune function and acts as an antioxidant that protects cells from damage 19. Most people do not need vitamin supplements.
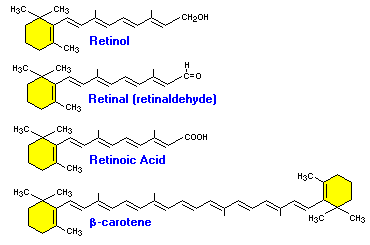



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vitamin-a-58b602a35f9b5860464ca3cf.png)